[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-07-1 Tips
Reminder : Maximum Likelihood Estimation
- Likelihood : 가능도, 우도
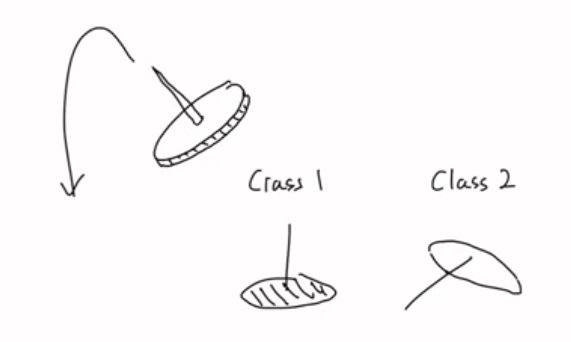
압정을 던졌을 때의 상황 가정
class 1. 납작한 면이 떨어지는 경우
class 2. 아닐 경우
각 class에 대한 확률분포가 존재함 → 확률을 인공지능을 통해 예측하고 싶다
예측해야 하는 값은 class1, class2 두개 → 베르누이 분포(이항분포) 가 된다
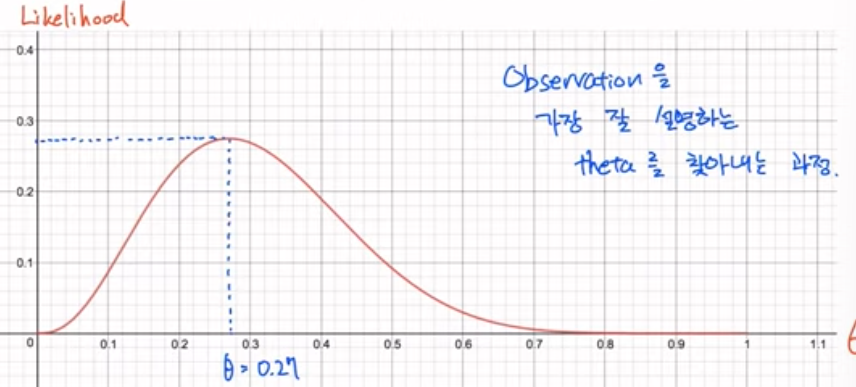
100번 압정을 던졌을 때 class1 이 27번 나옴
- observation(관찰값) : N=100, K=27
Binomial distribution
$K \sim \mathcal{B}(n, \theta)$
$P(K = k) = \binom{n}{k} \theta^k (1 - \theta)^{n - k}= \frac{n!}{k!(n - k)!} \cdot \theta^k (1 - \theta)^{n - k}$
에서 $\theta$는 압정의 확률분포를 결정하는 파라미터 값
이를 이용해 $f(\theta)$ 를 구할 수 있음
이 함수에서 $\theta$ 에 따른 값이 Likelihood
$\theta$를 탐색하면서 Likelihood가 Maximize되는 곳을 찾아야 함
이 과정이 MLE
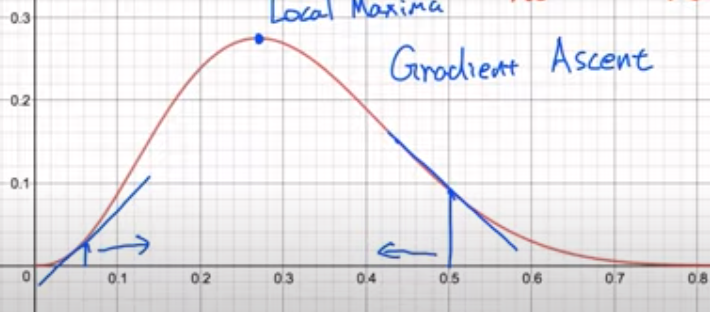
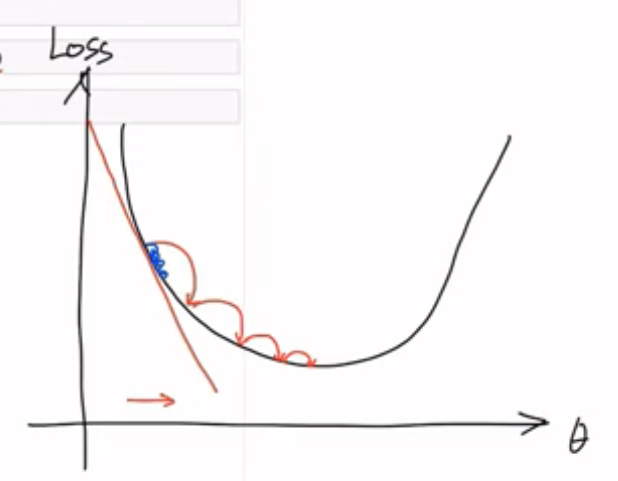
Reminder : Optimization via Gradient Descent
MLE를 찾기 위해서 기울기를 구함
기울기가 0이 되는 최대 값을 찾아야 되므로 Gradient Ascent 를 수행함
- Gradient Descent : 동일한 과정을 거쳐 최소 값을 찾는 과정
Reminder : Overfitting and Regrularization
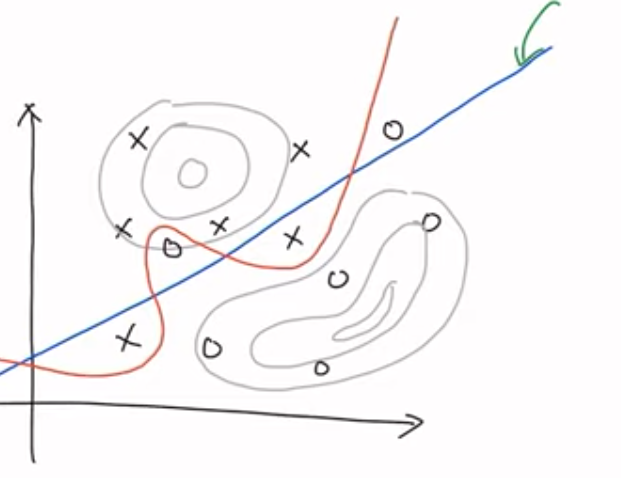
Overfitting
- MLE는 Overfitting이 숙명적으로 따라옴
- O / X 를 구분하는 선을 찾을 때 우리가 수집한 데이터가 모든 O, X의 확률 밀도를 나타낼 수 없음
- 주어진 데이터에 대해 과도하게 fitting 되어버림
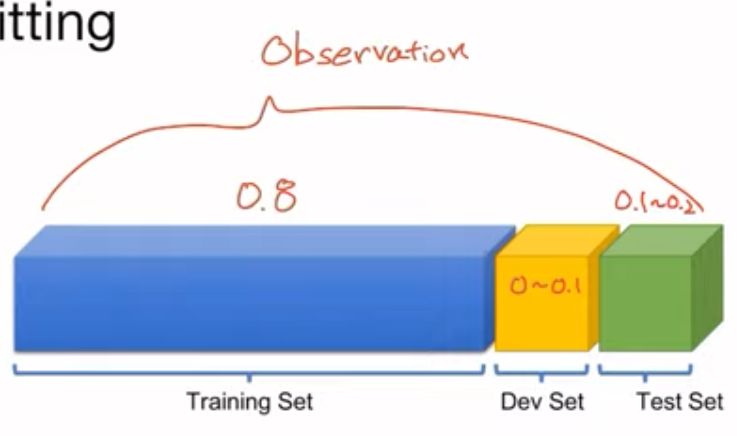
Training and Test Dataset
- overfitting을 최소화 하기위한 방법
- Training set, Test set, Dev set(= Validation set)으로 데이터를 나눔
- Training set에 과도하게 학습되어 버리면 Test set에서 좋은 성능이 나오지 않음
- Training set 학습 후 Test set에서 좋은 성능의 모델을 선택하는 작업을 반복할 경우 결과적으로 Training set, Test set 모두 overfitting될 수 있음
- Dev set은 Test set에 대해 과적합을 방지해줌
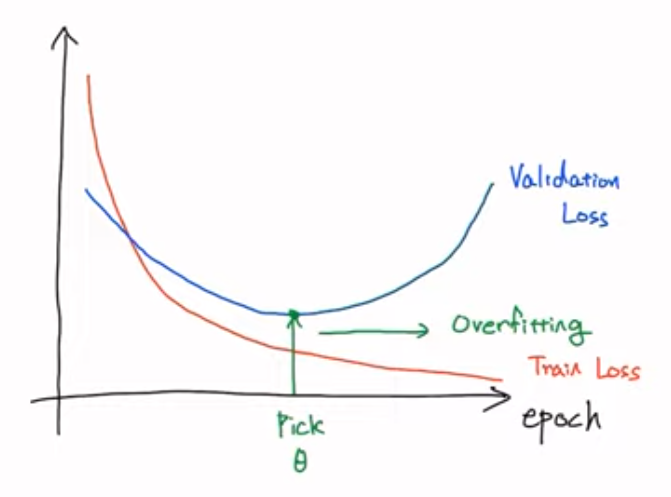
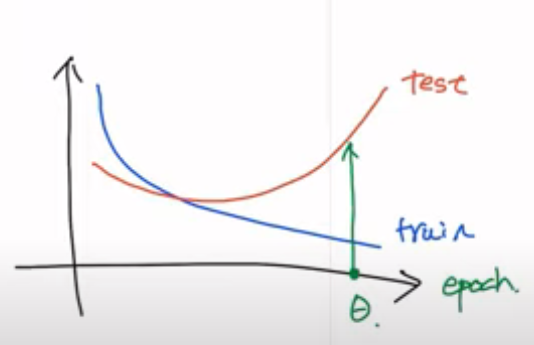
Train Loss는 epoch가 많아질수록 낮아짐
Validation Loss는 감소하다가 어느순간 증가하게 됨
두 Loss간 거리가 벌어지게 됨 → Overfitting
Validation Loss가 커지기 시작하면 훈련을 중단할 수 있음
이 외에 Overfitting 방지법
- 데이터를 많이 수집
- feature(데이터의 특징)를 적게 사용함
- Regularization 사용
- Early Stopping : Validation Loss가 더이상 낮아지지 않을 때
- Reducing Network Size : 딥러닝에서 유용한 방법
- Weight Decay : NN의 weight params 크기를 제한
- Dropout
- Batch Normalization
실습하기
- Training and Test Datasets
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# train
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2, 1],
[1, 3, 2],
[1, 3, 4],
[1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5],
[1, 2, 5],
[1, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7]
])
y_train = torch.LongTensor([2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0])
# test
x_test = torch.FloatTensor([[2, 1, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 3, 4]])
y_test = torch.LongTensor([2, 2, 2])
- Model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class SoftmaxClassifierModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(3, 3)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
# optimizer 설정
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
- Training
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train):
nb_epochs = 20
for epoch in range(nb_epochs):
# H(x) 계산
prediction = model(x_train)
# cost 계산
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_train)
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))
train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train)
- Test (Validation)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def test(model, optimizer, x_test, y_test):
prediction = model(x_test)
predicted_classes = prediction.max(1)[1]
correct_count = (predicted_classes == y_test).sum().item()
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_test)
print('Accuracy: {}% Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
correct_count / len(y_test) * 100, cost.item()
))
Learning Rate
Gradient Descent 에서의 $\alpha$ 값
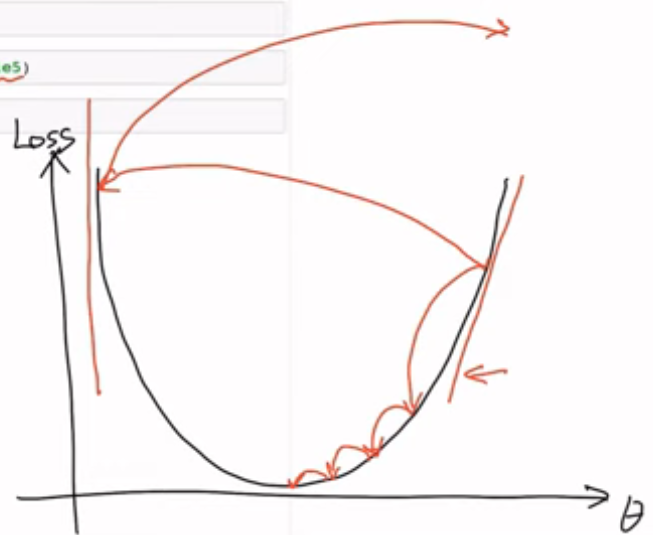
- learning rate이 너무 크면 diverge 하면서 cost 가 점점 늘어남 (overshooting, 발산)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e5)
train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train)
# Epoch 0/20 Cost: 1.280268
# Epoch 1/20 Cost: 976950.812500
# Epoch 2/20 Cost: 1279135.125000
# Epoch 3/20 Cost: 1198379.000000
# Epoch 4/20 Cost: 1098825.875000
# Epoch 5/20 Cost: 1968197.625000
# Epoch 6/20 Cost: 284763.250000
# Epoch 7/20 Cost: 1532260.125000
# Epoch 8/20 Cost: 1651504.000000
# Epoch 9/20 Cost: 521878.500000
# Epoch 10/20 Cost: 1397263.250000
# Epoch 11/20 Cost: 750986.250000
# Epoch 12/20 Cost: 918691.500000
# Epoch 13/20 Cost: 1487888.250000
# Epoch 14/20 Cost: 1582260.125000
# Epoch 15/20 Cost: 685818.062500
# Epoch 16/20 Cost: 1140048.750000
# Epoch 17/20 Cost: 940566.500000
# Epoch 18/20 Cost: 931638.250000
# Epoch 19/20 Cost: 1971322.625000
- learning rate이 너무 작으면 cost가 거의 줄어들지 않음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-10)
train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train)
# Epoch 0/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 1/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 2/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 3/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 4/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 5/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 6/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 7/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 8/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 9/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 10/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 11/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 12/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 13/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 14/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 15/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 16/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 17/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 18/20 Cost: 3.187324
# Epoch 19/20 Cost: 3.187324
- 데이터와 모델에 따라 굉장히 달라질 수 있어서 일반적인 값이 없음
- 적절한 숫자로 시작해 발산하면 작게, cost가 줄어들지 않으면 크게 조정
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train)
# Epoch 0/20 Cost: 1.341573
# Epoch 1/20 Cost: 1.198802
# Epoch 2/20 Cost: 1.150877
# Epoch 3/20 Cost: 1.131977
# Epoch 4/20 Cost: 1.116242
# Epoch 5/20 Cost: 1.102514
# Epoch 6/20 Cost: 1.089676
# Epoch 7/20 Cost: 1.077479
# Epoch 8/20 Cost: 1.065775
# Epoch 9/20 Cost: 1.054511
# Epoch 10/20 Cost: 1.043655
# Epoch 11/20 Cost: 1.033187
# Epoch 12/20 Cost: 1.023091
# Epoch 13/20 Cost: 1.013356
# Epoch 14/20 Cost: 1.003968
# Epoch 15/20 Cost: 0.994917
# Epoch 16/20 Cost: 0.986189
# Epoch 17/20 Cost: 0.977775
# Epoch 18/20 Cost: 0.969660
# Epoch 19/20 Cost: 0.961836
Data Preprocessing (데이터 전처리)
Gradient Descent를 통해 최적화를 수행하도록 데이터를 미리 학습하기 쉽게 해야 함
1
2
3
4
5
6
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[73, 80, 75],
[93, 88, 93],
[89, 91, 90],
[96, 98, 100],
[73, 66, 70]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[152], [185], [180], [196], [142]])
- σ : standard deviation (정규분포화)
- μ : 평균값
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
mu = x_train.mean(dim=0)
sigma = x_train.std(dim=0)
norm_x_train = (x_train - mu) / sigma # ~N(0, 1)
print(norm_x_train)
# tensor([[-1.0674, -0.3758, -0.8398],
# [ 0.7418, 0.2778, 0.5863],
# [ 0.3799, 0.5229, 0.3486],
# [ 1.0132, 1.0948, 1.1409],
# [-1.0674, -1.5197, -1.2360]])
Training with Preprocessed Data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
class MultivariateLinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(3, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
model = MultivariateLinearRegressionModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
def train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train):
nb_epochs = 20
for epoch in range(nb_epochs):
# H(x) 계산
prediction = model(x_train)
# cost 계산
cost = F.mse_loss(prediction, y_train)
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))
train(model, optimizer, norm_x_train, y_train)
# Epoch 0/20 Cost: 29785.091797
# Epoch 1/20 Cost: 18906.164062
# Epoch 2/20 Cost: 12054.674805
# Epoch 3/20 Cost: 7702.029297
# Epoch 4/20 Cost: 4925.733398
# Epoch 5/20 Cost: 3151.632568
# Epoch 6/20 Cost: 2016.996094
# Epoch 7/20 Cost: 1291.051270
# Epoch 8/20 Cost: 826.505310
# Epoch 9/20 Cost: 529.207336
# Epoch 10/20 Cost: 338.934204
# Epoch 11/20 Cost: 217.153549
# Epoch 12/20 Cost: 139.206741
# Epoch 13/20 Cost: 89.313782
# Epoch 14/20 Cost: 57.375462
# Epoch 15/20 Cost: 36.928429
# Epoch 16/20 Cost: 23.835772
# Epoch 17/20 Cost: 15.450428
# Epoch 18/20 Cost: 10.077808
# Epoch 19/20 Cost: 6.633700
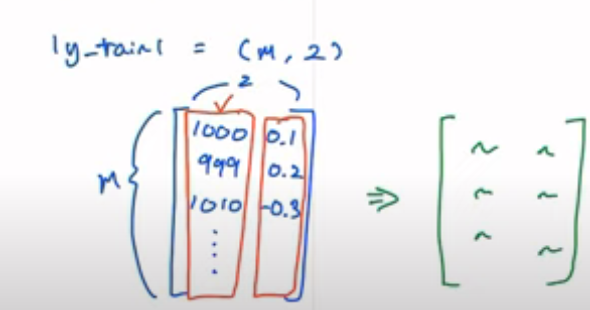
이미지와 같이 y_train이 2차원 값일 경우 뒤의 값은 매우 작은 부분이라 전처리를 하지 않으면 앞의 값에 편향되서 학습됨