[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-07-2 MNIST Introduction
[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-07-2 MNIST Introduction
What is MNIST?
- 0~9까지 손으로 쓴 숫자로 구성된 데이터셋
- 우체국에서 우편번호를 자동으로 인식하기 위해 만들어짐
- 6만장 Train data, labes + 1만장 Test data, labels
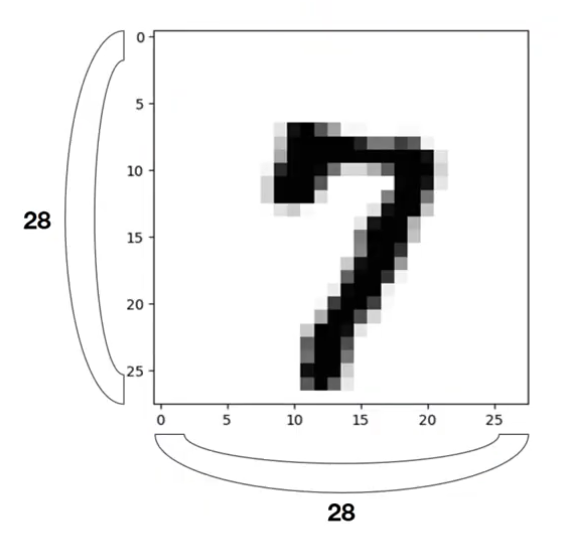
Example of MNIST
- 28 x 28 이미지
- 1 channel gray image (흑백)
- 28 x 28 값으로 이루어짐
- 784개의 데이터
- pytorch 에서 X = X.view(-1, 28 * 28)를 이용해 사용
- 0 ~ 9 digits
torchvision
- pytorch에서 사용하는 패키지
- datasets : NMIST, IMAGENET 등 데이터 셋
- models : Alexnet, VGG 등 모델 아키텍쳐
- Transforms : 데이터에 적용할 수 있는 transform(전처리)
- utils : 데이터를 쉽게 읽어오게 함
Reading data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
...
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(root="MNIST_data/", train=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), download=True)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(root="MNIST_data/", train=False, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), download=True)
...
# pytorch의 이미지는 0-1의 C,H,W 순서 값
# 일반적인 이미지는 0-255의 H,W,C 순서 값
# 이를 transforms.ToTenser()를 이용해 변환
data_loader = torch.utils.DataLoader(DataLoader=mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
# drop_last = batch size 만큼 데이터를 불러오고 남은 데이터를 가져올 지 설정
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
...
for X, Y in data_loader:
# X : MNIST 이미지
# Y : label (0~9)
X = X.view(-1, 28 * 28).to(device)
# view를 이용해 (batch size, 1(channel), 28, 28) -> (batch size, 784) 로 변경
# epoch : Training set 전체를 학습하는 횟수
# batch size : data set을 나누는 크기
# iteration : batch를 이용해 학습하는 횟수
Softmax
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# MNIST data image of shape 28 * 28 = 784
linear = torch.nn.Linear(784, 10, bias=True).to(device)
# parameters
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# define cost/loss & optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # Softmax is internally computed.
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(linear.parameters(), lr=0.1)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
total_batch = len(data_loader)
for X, Y in data_loader:
# reshape input image into [batch_size by 784]
# label is not one-hot encoded
X = X.view(-1, 28 * 28).to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = linear(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
# Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.535468459
# Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.359274179
# Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.331187546
# Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.316578031
# Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.307158172
# Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.300180733
# Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.295130193
# Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.290851533
# Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.287417084
# Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.284379542
# Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.281825215
# Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.279800713
# Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.277808994
# Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.276154280
# Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.274440825
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Test the model using test sets
with torch.no_grad(): # gradient 계산 x
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
prediction = linear(X_test)
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())
# Accuracy: 0.8862999677658081
Visualization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
r = random.randint(0, len(mnist_test) - 1)
X_single_data = mnist_test.test_data[r:r + 1].view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_single_data = mnist_test.test_labels[r:r + 1].to(device)
print('Label: ', Y_single_data.item())
single_prediction = linear(X_single_data)
print('Prediction: ', torch.argmax(single_prediction, 1).item())
plt.imshow(mnist_test.test_data[r:r + 1].view(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()
# Label: 8
# Prediction: 3
실습 전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# for reproducibility
random.seed(777)
torch.manual_seed(777)
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
# parameters
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# MNIST dataset
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=False,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# dataset loader
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=mnist_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True)
# MNIST data image of shape 28 * 28 = 784
linear = torch.nn.Linear(784, 10, bias=True).to(device)
# define cost/loss & optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # Softmax is internally computed.
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(linear.parameters(), lr=0.1)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
total_batch = len(data_loader)
for X, Y in data_loader:
# reshape input image into [batch_size by 784]
# label is not one-hot encoded
X = X.view(-1, 28 * 28).to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = linear(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning finished')
# Test the model using test sets
with torch.no_grad():
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
prediction = linear(X_test)
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, len(mnist_test) - 1)
X_single_data = mnist_test.test_data[r:r + 1].view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_single_data = mnist_test.test_labels[r:r + 1].to(device)
print('Label: ', Y_single_data.item())
single_prediction = linear(X_single_data)
print('Prediction: ', torch.argmax(single_prediction, 1).item())
plt.imshow(mnist_test.test_data[r:r + 1].view(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()
# Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.535150588
# Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.359577775
# Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.331264257
# Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.316404670
# Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.307106972
# Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.300456554
# Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.294933408
# Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.290956199
# Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.287074089
# Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.284515619
# Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.281914085
# Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.279526860
# Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.277636588
# Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.275874794
# Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.274422765
# Learning finished
# Accuracy: 0.8883000016212463
# Label: 8
# Prediction: 3
실습 코드 MNIST 오류상황
- MNIST 다운로드 오류
- 홈페이지에 직접 들어가서 다운받아도 403 오류 발생
- 터미널에서
!wget [www.di.ens.fr/~lelarge/MNIST.tar.gz](http://www.di.ens.fr/~lelarge/MNIST.tar.gz)와!tar -zxvf MNIST.tar.gz입력 - MNIST_data 폴더 안에 MNIST 데이터 직접 추가
- MNIST_data/MNIST/processed/training.pt is a zip archive (did you mean to use torch.jit.load()?) 오류
- torch 1.6버전 이하에서 발생하는 문제
- pip install –upgrade torch 로 pytorch 업그레이드
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.