[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-08-1 Perceptron
[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-08-1 Perceptron
인공신경망
- 동물의 신경계 (뇌의 뉴런) 의 동작방식을 본따 만든 모델
Nueron
- 뇌에서 신호를 주고받는 역할
- 입력신호의 총 크기가 특정값(threshhold)을 넘으면 다음 뉴런으로 전파되는 간단한 구조
Perceptron
- 인공신경망 한 종류
- 입력 x들에 대해 $\sum {x*w(weight)+b(bias)}$ 를 통해 output을 출력
- output은 활성화 함수(activation funtion) 거쳐서 만들어짐
- 초창기 퍼셉트론은 Linear Classifier를 위해 만들어짐 (개,고양이 분류)
Activation funtion(활성화 함수)
뉴런의 출력 값을 결정하는 비선형 함수
신경망에 비선형성을 부여해 복잡한 패턴을 학습할 수 있게 함
ex ) sigmoid, ReLU, tanh
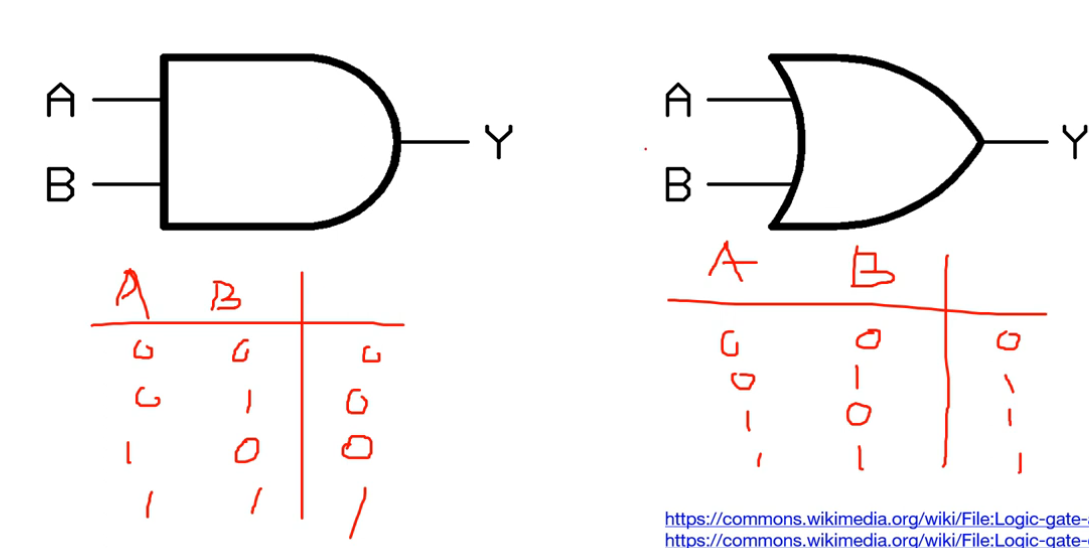
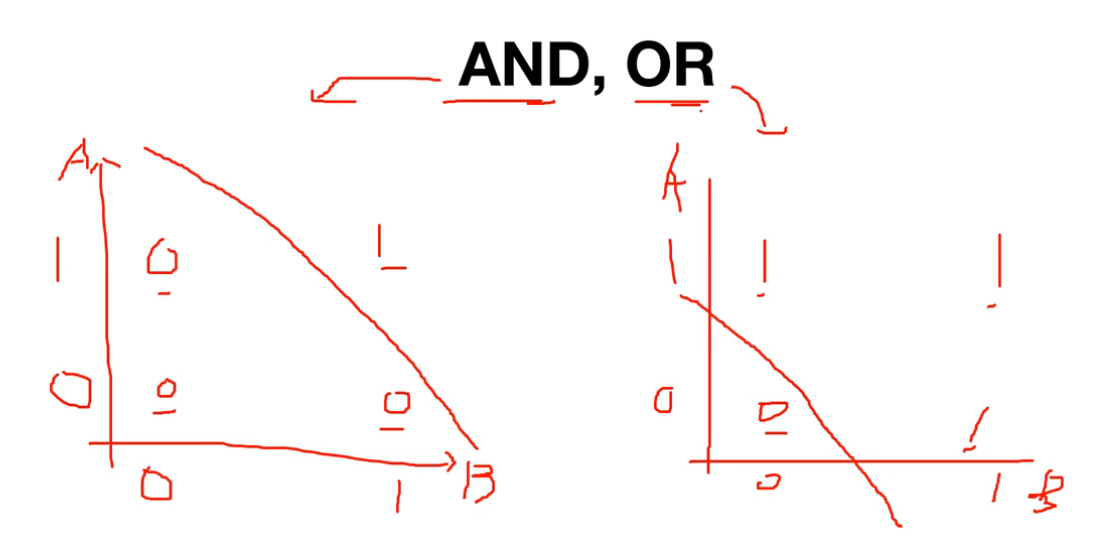
AND, OR
- AND : 두 입력 A, B 모두 1일 때만 1을 출력, 나머지 0 출력
- OR : 두 입력 A, B 모두 0일 때만 0을 출력, 나머지 1 출력
- 퍼셉트론은 이러한 AND, OR 문제를 Linear Classicification을 통해 간단하게 분류 가능
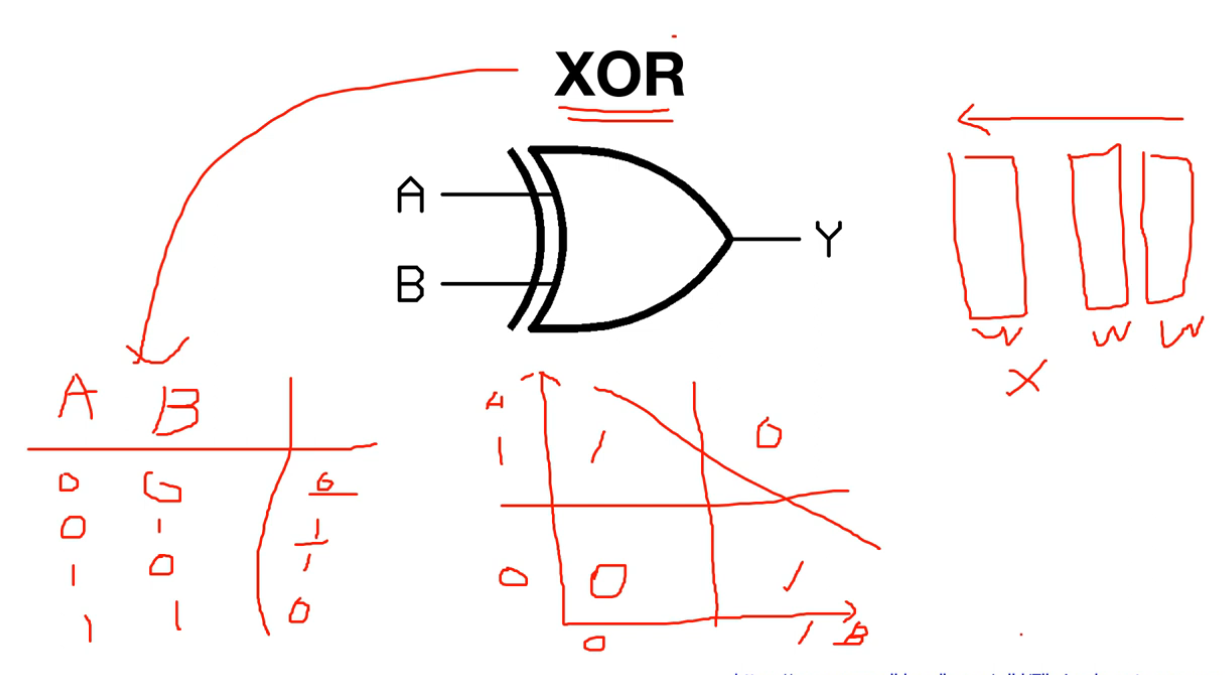
XOR
- AND, OR 문제를 해결한 후 NN을 통해 더 복잡한 문제 해결을 기대
- 하지만 한개의 layer를 가지는 퍼셉트론 구조로는 XOR를 해결할 수 없고, multi layer가 필요하지만, multi layer의 가중치 학습 방법이 없다는 것이 증명됨
- 이후 multi layer를 학습시킬 수 있는 Backpropagation(역전파) 방법이 개발되어 XOR 문제 해결이 가능해짐
퍼셉트론으로는 Linear Classification으로 나누는 것이 불가능함
→ 퍼셉트론은 비선형 문제를 해결하는데 한계가 있음
Code : XOR
- 200 step 이후로 학습이 제대로 되지 않고 loss가 일정하게 나옴
- 학습이 끝난 후 Hypothesis를 출력하면 모든 값을 0.5 예측함
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
import torch
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(777)
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
# XOR
X = torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]).to(device)
Y = torch.FloatTensor([[0], [1], [1], [0]]).to(device)
# nn layers
linear = torch.nn.Linear(2, 1, bias=True) #layer
sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid() #활성화 함수
# model
model = torch.nn.Sequential(linear, sigmoid).to(device)
# define cost/loss & optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1)
#학습
for step in range(10001):
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = model(X)
# cost/loss function
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, cost.item())
# 0 0.7273974418640137
# 100 0.6931476593017578
# 200 0.6931471824645996
# 300 0.6931471824645996
# ...
# 9800 0.6931471824645996
# 9900 0.6931471824645996
# 10000 0.6931471824645996
# Accuracy computation
# True if hypothesis>0.5 else False
with torch.no_grad():
hypothesis = model(X)
predicted = (hypothesis > 0.5).float()
accuracy = (predicted == Y).float().mean()
print('\nHypothesis: ', hypothesis.detach().cpu().numpy(), '\nCorrect: ', predicted.detach().cpu().numpy(), '\nAccuracy: ', accuracy.item())
# Hypothesis: [[0.5]
# [0.5]
# [0.5]
# [0.5]]
# Correct: [[0.]
# [0.]
# [0.]
# [0.]]
# Accuracy: 0.5
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.