[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-10-2 mnist cnn
[모두를 위한 딥러닝 시즌2] Lab-10-2 mnist cnn
딥러닝 학습 단계
- 반드시 순서를 따라야 하는 것은 아니다
- GPU가 없을 경우 CPU로 대체하여 연산
- 라이브러리를 가져온다(torch, torchvision, matplotlib 등)
- GPU 사용 설정 및 random value를 위한 seed 설정
- 학습 parameter 설정(learning_rate, training_epochs, batch_size 등)
- dataset 가져오고 loader 만들기
- 학습 모델 만들기 (class CNN(torch.nn.Module))
- Loss function (Criterion) 와 최적화 도구(optimizer) 선택
- 모델 학습 및 loss check(Criterion의 output)
- 학습된 모델의 성능 확인
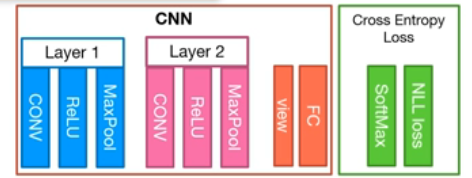
CNN 구조
- Layer 1
- Convolution layer = (in_c = 1, out_c = 32, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, padding = 1)
- MaxPool layer = (kernel_size = 2, stride = 2)
- Layer 2
- Convolution layer = (in_c = 32, out_c = 64, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, padding = 1)
- MaxPool layer = (kernel_size = 2, stride = 2)
- View
- batch_size * [7,7,64] ⇒ batch_size * [3136]
- Fully_Connect layer
- input = 3136, output = 10
MNIST CNN Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn.init
# GPU 사용 가능 여부 확인
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 재현성을 위해 랜덤 시드 설정
torch.manual_seed(777)
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
# 하이퍼파라미터 설정
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# MNIST 데이터셋 다운로드 및 불러오기 (훈련 데이터)
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(
root='MNIST_data/', # 데이터를 저장할 경로
train=True, # 훈련 데이터 여부
transform=transforms.ToTensor(), # 데이터를 텐서 형태로 변환
download=True # 다운로드 여부
)
# MNIST 데이터셋 다운로드 및 불러오기 (테스트 데이터)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(
root='MNIST_data/',
train=False, # 테스트 데이터 여부
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
# 데이터 로더 생성 (훈련 데이터셋을 배치 단위로 로드)
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=mnist_train, # 데이터셋
batch_size=batch_size, # 배치 크기
shuffle=True, # 데이터를 섞을지 여부
drop_last=True # 마지막 배치를 버릴지 여부 (배치 크기가 부족할 때)
)
# CNN 모델 정의
class CNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
# 첫 번째 컨볼루션 레이어 (입력: 1채널, 출력: 32채널, 커널 크기: 3x3)
# L1 ImgIn shape=(?, 28, 28, 1)
# Conv -> (?, 28, 28, 32)
# Pool -> (?, 14, 14, 32)
self.layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), # 출력 크기: 28x28x32
torch.nn.ReLU(), # 활성화 함수
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 풀링 후 크기: 14x14x32
)
# 두 번째 컨볼루션 레이어 (입력: 32채널, 출력: 64채널, 커널 크기: 3x3)
# L2 ImgIn shape=(?, 14, 14, 32)
# Conv ->(?, 14, 14, 64)
# Pool ->(?, 7, 7, 64)
self.layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), # 출력 크기: 14x14x64
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 풀링 후 크기: 7x7x64
)
# 완전 연결 레이어 (입력: 7x7x64, 출력: 10)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(7 * 7 * 64, 10, bias=True)
# Xavier 초기화로 가중치 초기화
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc.weight)
def forward(self, x):
# 첫 번째 레이어 통과
out = self.layer1(x)
# 두 번째 레이어 통과
out = self.layer2(out)
# 완전 연결 레이어를 위해 텐서를 평탄화
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
# 완전 연결 레이어 통과
out = self.fc(out)
return out
# CNN 모델 인스턴스화 및 장치로 이동
model = CNN().to(device)
# 손실 함수 및 최적화 알고리즘 정의
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # 크로스 엔트로피 손실 함수 (내부적으로 Softmax 포함)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # Adam 옵티마이저
# 모델 학습
total_batch = len(data_loader) # 총 배치 수
print('Learning started. It takes sometime.')
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0 # 에포크당 평균 손실
for X, Y in data_loader:
# 입력 데이터와 라벨 데이터를 장치로 이동
X = X.to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
# 옵티마이저 초기화
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 모델 예측
hypothesis = model(X)
# 손실 계산
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
# 손실 역전파
cost.backward()
# 모델 매개변수 업데이트
optimizer.step()
# 배치 손실을 평균 손실에 더함
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
# 에포크마다 손실 출력
print('[Epoch: {:>4}] cost = {:>.9}'.format(epoch + 1, avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# [Epoch: 1] cost = 0.225939184
# [Epoch: 2] cost = 0.0630982518
# [Epoch: 3] cost = 0.0463336967
# [Epoch: 4] cost = 0.0374494195
# [Epoch: 5] cost = 0.0313653052
# [Epoch: 6] cost = 0.0261803828
# [Epoch: 7] cost = 0.0218190774
# [Epoch: 8] cost = 0.0183058828
# [Epoch: 9] cost = 0.0164249353
# [Epoch: 10] cost = 0.0131303286
# [Epoch: 11] cost = 0.00988870859
# [Epoch: 12] cost = 0.00991326477
# [Epoch: 13] cost = 0.00879074447
# [Epoch: 14] cost = 0.0067628026
# [Epoch: 15] cost = 0.00727953995
# 모델 테스트 및 정확도 계산
with torch.no_grad(): # 테스트 단계에서는 기울기 계산 비활성화
# 테스트 데이터를 모델에 입력하기 위한 전처리
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(len(mnist_test), 1, 28, 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
# 테스트 데이터에 대한 예측
prediction = model(X_test)
# 예측 값과 실제 라벨 비교
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
# 정확도 계산
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())
# Accuracy: 0.9873999953269958
- Accuracy(정확도) : 98.7%
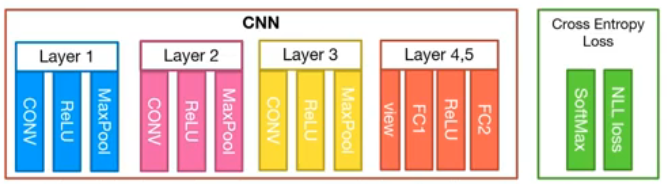
더 깊은 CNN 구조
- Layer 1
- Convolution layer = (in_c = 1, out_c = 32, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, padding = 1)
- MaxPool layer = (kernel_size = 2, stride = 2)
- Layer 2
- Convolution layer = (in_c = 32, out_c = 64, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, padding = 1)
- MaxPool layer = (kernel_size = 2, stride = 2)
- Layer 3
- Convolution layer = (in_c = 64, out_c = 128, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, padding = 1)
- MaxPool layer = (kernel_size = 2, stride = 2)
- Layer 4
- Fully_Connect layer = (input = 4 * 4 * 128, output = 625)
- Layer 5
- Fully_Connect layer = (input = 625, output = 10)
MNIST CNN Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
# Lab 11 MNIST and Deep learning CNN
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn.init
# GPU 사용 가능 여부 확인
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 재현성을 위한 랜덤 시드 설정
torch.manual_seed(777)
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
# 하이퍼파라미터 설정
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# MNIST 데이터셋 다운로드 및 로드 (훈련 데이터)
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(
root='MNIST_data/', # 데이터를 저장할 경로
train=True, # 훈련 데이터 여부
transform=transforms.ToTensor(), # 데이터를 텐서 형태로 변환
download=True # 다운로드 여부
)
# MNIST 데이터셋 다운로드 및 로드 (테스트 데이터)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(
root='MNIST_data/',
train=False, # 테스트 데이터 여부
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
# 데이터 로더 생성 (훈련 데이터를 배치 단위로 로드)
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=mnist_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, # 데이터를 섞음
drop_last=True # 마지막 배치를 버림 (배치 크기가 부족할 때)
)
# CNN 모델 정의
class CNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.keep_prob = 0.5 # 드롭아웃 확률
# L1: Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool (입력: 28x28x1, 출력: 14x14x32)
self.layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# L2: Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool (입력: 14x14x32, 출력: 7x7x64)
self.layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# L3: Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool (입력: 7x7x64, 출력: 4x4x128)
self.layer3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# L4: Fully Connected -> ReLU -> Dropout (입력: 4x4x128, 출력: 625)
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(4 * 4 * 128, 625, bias=True)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc1.weight) # Xavier 초기화
self.layer4 = torch.nn.Sequential(
self.fc1,
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Dropout(p=1 - self.keep_prob) # 드롭아웃 적용
)
# L5: Fully Connected (입력: 625, 출력: 10)
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(625, 10, bias=True)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc2.weight)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = self.layer3(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) # FC 레이어를 위한 Flatten
out = self.layer4(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out
# CNN 모델 생성 및 장치로 이동
model = CNN().to(device)
# 손실 함수 및 옵티마이저 설정
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # 크로스 엔트로피 손실 함수 (Softmax 포함)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # Adam 옵티마이저
# 모델 학습
total_batch = len(data_loader) # 총 배치 수
model.train() # Dropout 활성화
print('Learning started. It takes some time.')
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0 # 에포크당 평균 손실
for X, Y in data_loader:
# 입력 데이터를 GPU/CPU 장치로 이동
X = X.to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
# 옵티마이저 초기화
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 모델 예측
hypothesis = model(X)
# 손실 계산
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
# 손실 역전파
cost.backward()
# 가중치 업데이트
optimizer.step()
# 배치 손실 누적
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
# 에포크 결과 출력
print('[Epoch: {:>4}] cost = {:>.9}'.format(epoch + 1, avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# [Epoch: 1] cost = 0.190638304
# [Epoch: 2] cost = 0.0532845221
# [Epoch: 3] cost = 0.037660379
# [Epoch: 4] cost = 0.0296484027
# [Epoch: 5] cost = 0.0239125956
# [Epoch: 6] cost = 0.0203637555
# [Epoch: 7] cost = 0.0181394033
# [Epoch: 8] cost = 0.0136777712
# [Epoch: 9] cost = 0.0135163562
# [Epoch: 10] cost = 0.0108031444
# [Epoch: 11] cost = 0.00989781693
# [Epoch: 12] cost = 0.0114726787
# [Epoch: 13] cost = 0.00667280518
# [Epoch: 14] cost = 0.00744756451
# [Epoch: 15] cost = 0.00912202988
# 모델 테스트
with torch.no_grad(): # 기울기 계산 비활성화
model.eval() # Dropout 비활성화
# 테스트 데이터를 모델에 입력
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(len(mnist_test), 1, 28, 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
# 테스트 데이터 예측
prediction = model(X_test)
# 예측값과 실제 라벨 비교
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
# 정확도 계산
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())
# Accuracy: 0.9837999939918518
- Accuracy : 98.3%
- Accuracy가 감소하는 모습을 보여줌
- 모델을 구성할 때 깊은 레이어도 중요하지만, 효율적으로 레이어를 구성하는 것이 더 중요
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.